Insulin isn’t always popular with diabetics: some are afraid of the injections and others think their condition is worse if insulin is suggested for them. By getting more information about insulin, we can demystify its use and enjoy its benefits.
What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone that is a part of the spectrum used to treat diabetes, which is characterized by the under-production of insulin by the pancreas or the deficient use of insulin by the organism. As a result, the blood glucose (sugar) level remains high and can cause damage to certain organs. The role of insulin is to enable glucose in the blood to enter the body’s cells to provide them with energy and rebalance the blood glucose level.
In the case of type 1 diabetes, there is not enough insulin secretion by the pancreas. So, insulin treatment is mandatory.
As for type 2 diabetes, it is firstly treated by:
- the adoption of healthy lifestyle habits (food, weight loss, physical activity);
- oral medications.
When these steps don’t result in a sufficient control of the blood glucose level, the introduction of insulin may be considered. This does not mean that your diabetes is more serious, but simply that adequate control of your blood glucose level has not been reached with your current treatment.
Types of insulin available on the market
A long time ago, the insulin used was extracted from a natural source such as cattle and pigs. Today, insulin is made in the laboratory. It is identical or nearly so to insulin secreted by the human pancreas.
Different types of insulin are classified according to their initial effect and the duration of their action. Some work quickly and for a few hours (rapid and ultra-rapid acting insulin) while others have a longer duration of action (long acting insulin).
Dosage and frequency of injections
The number of insulin injections required can range from one to four per day.
The insulin dose varies from one individual to another and can be influenced by various factors, particularly:
- the quantity of insulin produced by your body;
- your weight;
- your dietary habits;
- your level of physical activity;
- other medications that you take.
Your insulin treatment plan will be determined by your doctor or your specialized diabetes care team.
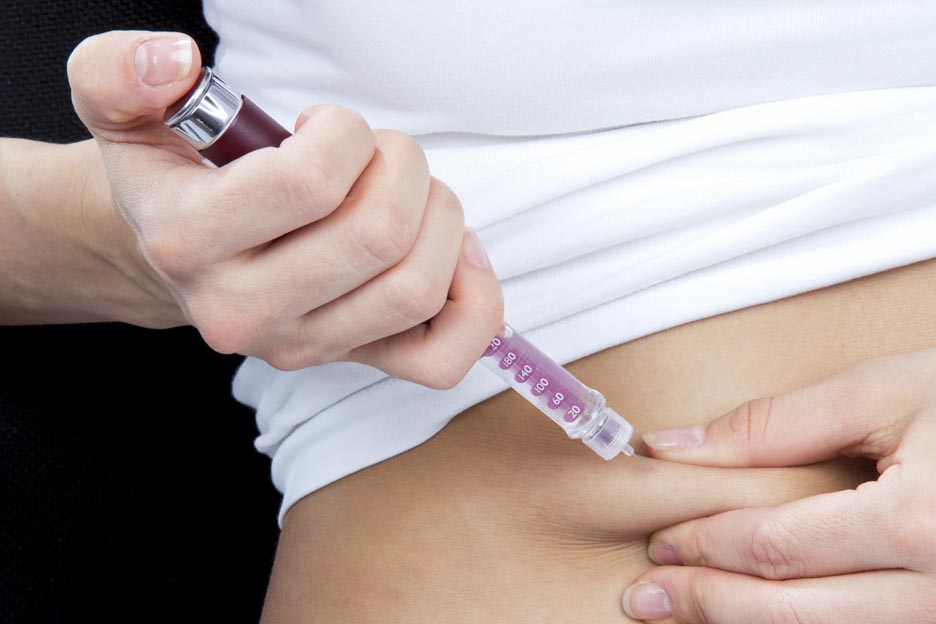
Proper injection for optimal effect
Insulin must be injected in the subcutaneous tissue (fat tissue directly under the skin), where it will be absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
Insulin cannot be taken orally because it is destroyed by the acid in the stomach. So, it will not be effective.
In general, people give themselves their insulin shots. There are three types of devices available for the administration of insulin injections:
- the syringe;
- the pen;
- the pump.
It is mostly type 1 diabetics who use the insulin pump, which is a small portable device that is connected by a tube inserted under the skin and delivers insulin continuously.
For the use of syringes and insulin pens, careful instruction must be given to the user because it is crucial to know the right techniques of injection, including possible injection sites, their rotation, and monitoring.
The industry is doing everything to offer insulin users the shortest and thinnest needles possible to give them greater comfort during their daily insulin injections. Also, it is important to use a fresh needle for each injection.
Insulin storage
Improperly stored insulin could result in badly controlled blood glucose levels. Insulin cartridges and vials must be stored in the refrigerator until their first use. Then, the cartridge or vial that you use every day can be kept at room temperature. It will be stable for a month.
Your insulin reserves must be kept in the refrigerator and can be used until the expiry date indicated by the manufacturer.
At all times, insulin must be kept away from sunlight, excessive heat, and freezing temperatures, which can degrade it and make it lose its potency.
The most frequent side-effect: hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is a significant drop in the blood sugar level. It can cause unpleasant symptoms such as perspiration, tremors, weakness, etc. It is the most common side-effect encountered by insulin users.
Certain conditions can lead to hypoglycemia, such as:
- an insulin dosage error;
- a meal too low in carbohydrates or skipping a meal;
- intense physical activity;
- the consumption of alcohol.
So, it is essential to self-monitor your blood glucose level every day as many times as recommended by your doctor. You can read your blood glucose levels using an instrument known as the blood glucose meter. Self-monitoring your blood glucose level helps you quickly identify moments of hypoglycemia and correct it without delay.
A few tips for the correct use of insulin
- Make sure you take the right dose.
- Do not change the prescribed dose, unless you have discussed it with your medical team and have been instructed on how to adjust your dose.
- Respect the right technique of injection (hygiene, rotation of injection sites, the form of your insulin, etc.).
- Measure your blood glucose level every day, as many times as your doctor has told you to.
- Bring your used needles in the containers provided to your pharmacy or your CLSC. You can also obtain disposal containers at these places.
What does the future hold?
The pharmaceutical industry has been relentless in its diabetes treatment research. Various pharmacological and technological avenues are being explored continuously for the discovery of new drugs, new ways of insulin administration, and to finalize pancreas transplantation or the use of genetically programmed cells.
These research efforts bring hope for people living with diabetes. Don’t hesitate to learn more about the subject. Discuss it with your pharmacist and your medical team. This can be a source of motivation!