Skin fungus (mycosis) can appear without warning and cause itching and discomfort. In this article, we’ll give you some advice and practical tips on how to get rid of it, prevent it from coming back, and keep your skin healthy.
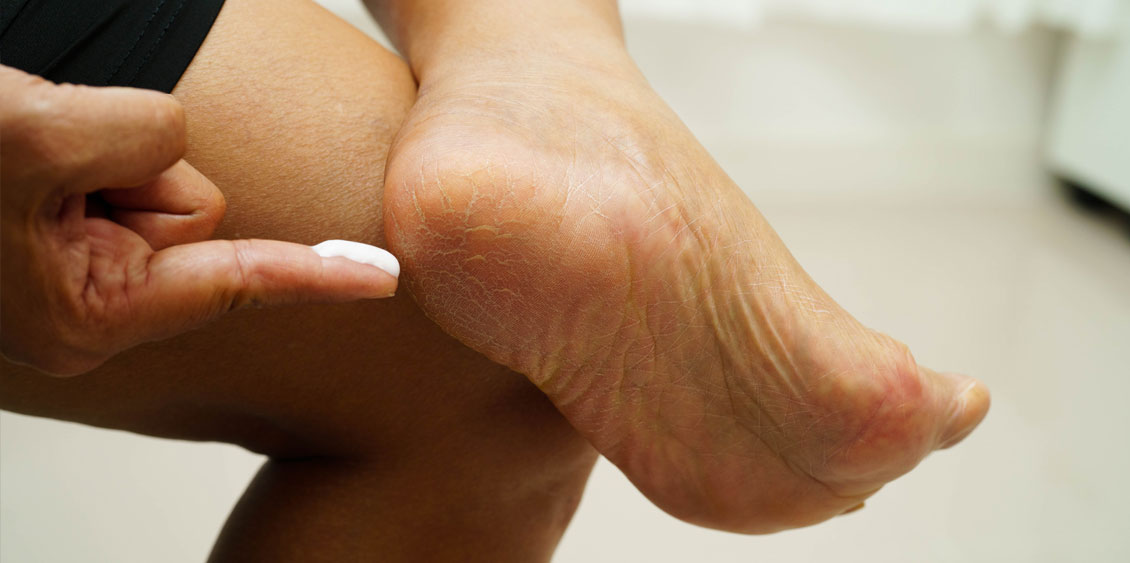
What is skin fungus?
Skin fungus is caused by a fungal infection—a growth of microscopic fungus—on the surface of the skin. Three families of fungus are responsible for fungal infections: dermatophytes (like Trichophyton), yeasts (like Candida), and mould. These organisms thrive in warm, damp places.
What parts of the body can be affected?
- Feet (athlete’s foot)
- Skin folds (intertrigo)
- Scalp (ringworm)
- Nails (onychomycosis)
These areas of the body are particularly favourable environments for fungal growth.
What are the symptoms of skin fungus?
The first warning signs are often:
- Persistent itching
- Localized redness, sometimes in the shape of a ring
- Scaly or oozing skin patches
- Painful cracks in the skin, especially between the toes
Note: If you’ve had these symptoms for several days, it’s best to seek a diagnosis. Your pharmacist can examine the area and, if necessary, refer you for a test (skin scraping or swab) to confirm the infection.
What causes light spots on the skin?
Light spots on the skin are typical of tinea versicolor, a fungal infection caused by the yeast Malassezia that generally develops on the torso, shoulders, or neck. These spots have blurred edges and may appear more prominent after sun exposure, as the surrounding skin tans, but the infected area does not.
Does tinea versicolor require a different treatment than other skin funguses?
Tinea versicolor is generally treated with the same families of antifungals as other fungal infections, but often in specific formulations for the body and scalp.
- Shampoo or lotion containing selenium sulfide or ketoconazole, applied to the body or scalp 2 or 3 times a week for 2 to 4 weeks.
- Cream or gel containing ketoconazole or clotrimazole, as a 7- to 28-day course of treatment if the infection is restricted to a small area of the skin.
An oral treatment may be prescribed on the advice of a physician for more widespread infections or recurring infections.
Advice: If you notice light patches like this (Tinea versicolor) on your skin after sun exposure, it's important to talk to your pharmacist. They may recommend treatment.
And don’t forget to apply sunscreen before spending time in the sun. You can learn which sunscreen is right for your skin type in our article.
Are fungal infections contagious?
Yes, fungal infections can be spread through direct contact (skin-to-skin) or indirect contact (sharing towels or shoes). It’s best not to share socks or bath towels (especially at the pool in the summer, for example) and to air out and disinfect your shoes regularly. These simple steps reduce the risk of spreading the infection to family members, colleagues, or strangers in public places.
What causes fungal infections?
Fungal infections are caused by a natural overgrowth of microorganisms (dermatophytes, yeast, or mould) that take up residence in warm, damp, and sometimes irritated skin (due to sweat, friction, microtears, etc.). When the balance of the skin’s microbiome is disrupted, fungi can proliferate and cause unpleasant symptoms.
What are the different types of skin fungus?
Athlete’s foot
Athlete’s foot causes dry or peeling skin between the toes, accompanied by intense itching.
Intertrigo
Intertrigo affects skin folds (often those in the groin and armpits) and causes a red, weeping rash to develop, often accompanied by a burning sensation.
Ringworm of the scalp
Ringworm of the scalp is characterized by the appearance of round, scaly patches, which can lead to hair loss.
Tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor causes light or dark spots to appear on the torso or, more rarely, the feet.
Nail fungus (onychomycosis)
Nail fungus affects the nails, which become thick, discoloured, and brittle.
Is skin fungus a serious condition?
Pas de panique! Une mycose cutanée n’est pas une maladie grave, mais elle peut vite devenir source de gêne et d’inconfort. Sans traitement, l’infection peut s’étendre à d’autres zones. Plus vous attendez, plus le champignon s’installe et plus le traitement sera long. Il est recommandé d’agir rapidement.
How long does it take to get rid of a fungal infection?
It depends on the location and severity of the infection. On average, it takes 2 to 4 weeks to treat athlete’s foot and up to 3 months to treat nail fungus. When treating skin fungus, patience is key: Even if the itching quickly subsides, the treatment must be continued until all signs and symptoms have cleared up to prevent recurrence.
How do you treat a fungal infection?
- With topical antifungals, such as creams, powders, or sprays containing clotrimazole, miconazole, or tolnaftate, which you can find in most pharmacies. Topical treatments must be applied daily to clean, dry skin, for the duration indicated on the label.
- With oral antifungals, which are generally used to treat more widespread or stubborn infections. They are usually prescribed by your doctor. Your pharmacist will explain any possible interactions and what precautions to take.
Are natural treatments effective?
You may have heard that you can treat skin fungus with tea tree oil, cider vinegar, or baking soda. While these products may provide additional relief, they are no substitute for a proven antifungal medication. It’s important to let your skin’s microbiome recover, and improperly administered home treatments can actually make the irritation worse.
Why won’t my skin fungus clear up even after treatment?
Poor hygiene, stopping treatment early, or a dirty environment could be the culprit. Here are 3 tips to ensure that your treatment is effective:
- Thoroughly clean your shoes, clothes, and linens
- Finish the full course of your treatment, even if your infection appears to have cleared up already
- Keep your skin dry
Prevention and good habits
How do you prevent fungal infections from coming back?
Here are a few good habits you can adopt to prevent a new fungal infection from ruining your day. Small steps add up to big results:
- Thoroughly dry the skin between your toes after showering
- Wear cotton or technical fibre socks and change them every day
- Air out your shoes for at least 24 hours before putting them back on
- Wear sandals in wet areas (e.g., pools and locker rooms)
When should you see a health care professional?
In some cases, fungal infections can become more serious. If you notice any of the following symptoms, it’s important to consult a health care professional:
- Fever or rapid expansion of the infected area
- Severe pain or signs of a bacterial infection (pus, swelling)
- Recurring infections despite appropriate treatment
Depending on the complexity of your case, your pharmacist may suggest a topical treatment first or refer you to a dermatologist.
Should you see a dermatologist or pharmacist?
First, we recommend that you consult your pharmacist for a quick diagnosis, first-line treatment, and practical advice. The pharmacist may recommend that you see a dermatologist if the infection is widespread, if it affects your scalp or nails, or if you have severe symptoms or risk factors.
Fungal infections can be prevented. With a few good habits and the right treatment, you can relieve your discomfort and get back to feeling like you. Your pharmacists are there to listen, advise, and support you at every stage of your recovery.
Other articles that might interest you
Vaginal yeast infections: 4 things to know
Athlete’s foot: how to recognize it, treat it, and prevent it